What are thermoplastic elastomers (TPE)?
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are innovative materials that can be processed like thermoplastics while exhibiting rubber-like properties.
What are thermoplastic elastomers?
Thermoplastic elastomers (abbreviation: TPE) are materials that can be processed thermoplastically while exhibiting rubber-like performance characteristics.
Thermoplastic elastomers are very easy to shape, as they pass through a plastic state during processing. They can be produced in almost any hardness. By modification, adhesion to nearly all technical thermoplastics can be achieved. Their flowability, density, appearance, scratch resistance, and other properties can also be adjusted through compounding with various fillers and additives.
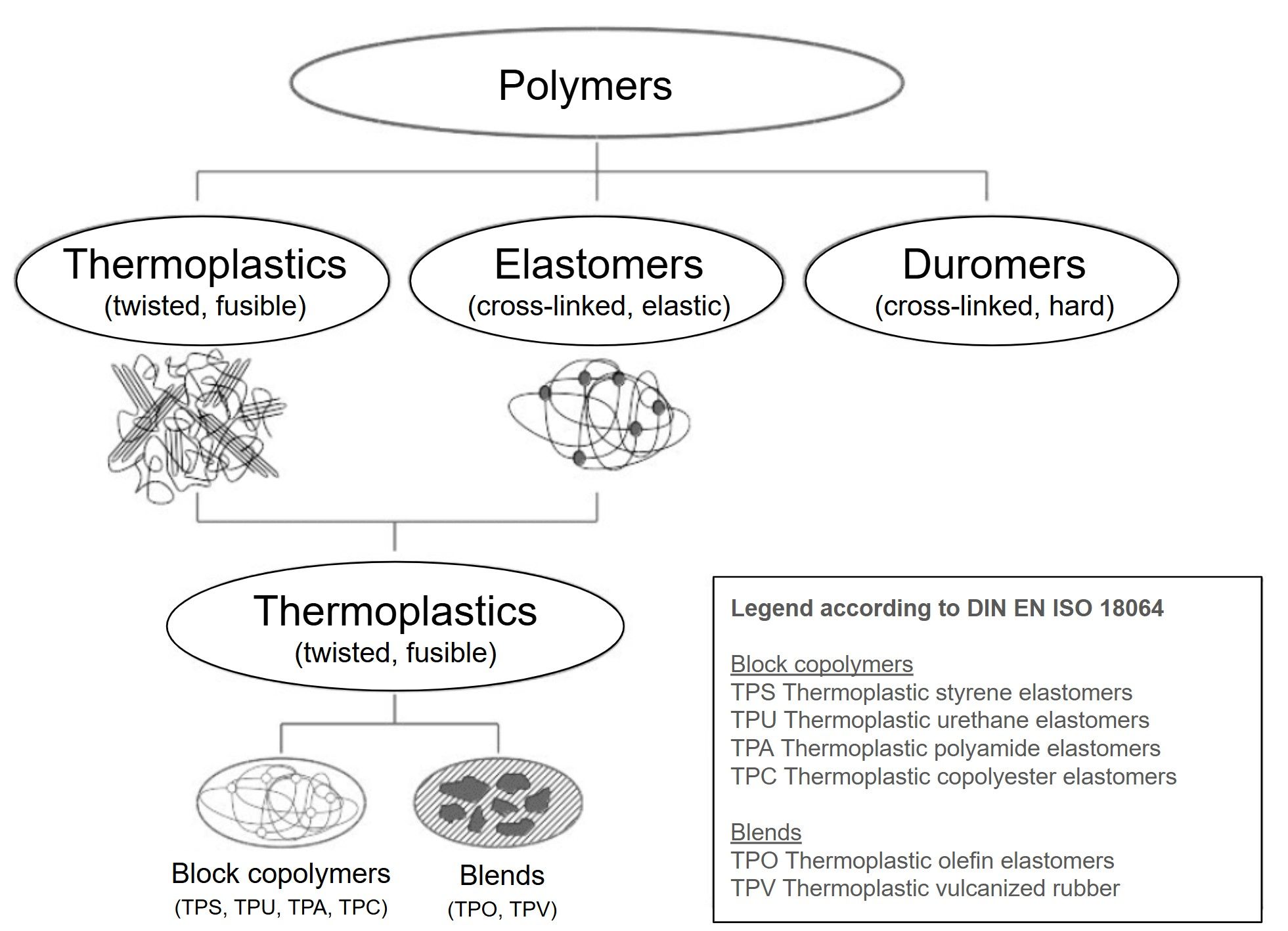
What types of TPE are there?
Thermoplastic elastomers can be divided into TPE blends and block copolymers.
Blends are alloys consisting of a plastic matrix and a soft material, such as an elastomer. Examples include TPO (thermoplastic olefin elastomer) and TPV (thermoplastic vulcanizate).
Block copolymers are molecular chains with different segments that form “hard” and “soft” domains when cooled. Examples include TPS (styrene block copolymer), TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane), TPC (thermoplastic polyester elastomer), and TPA (thermoplastic polyether polyamide).